JTM Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd.
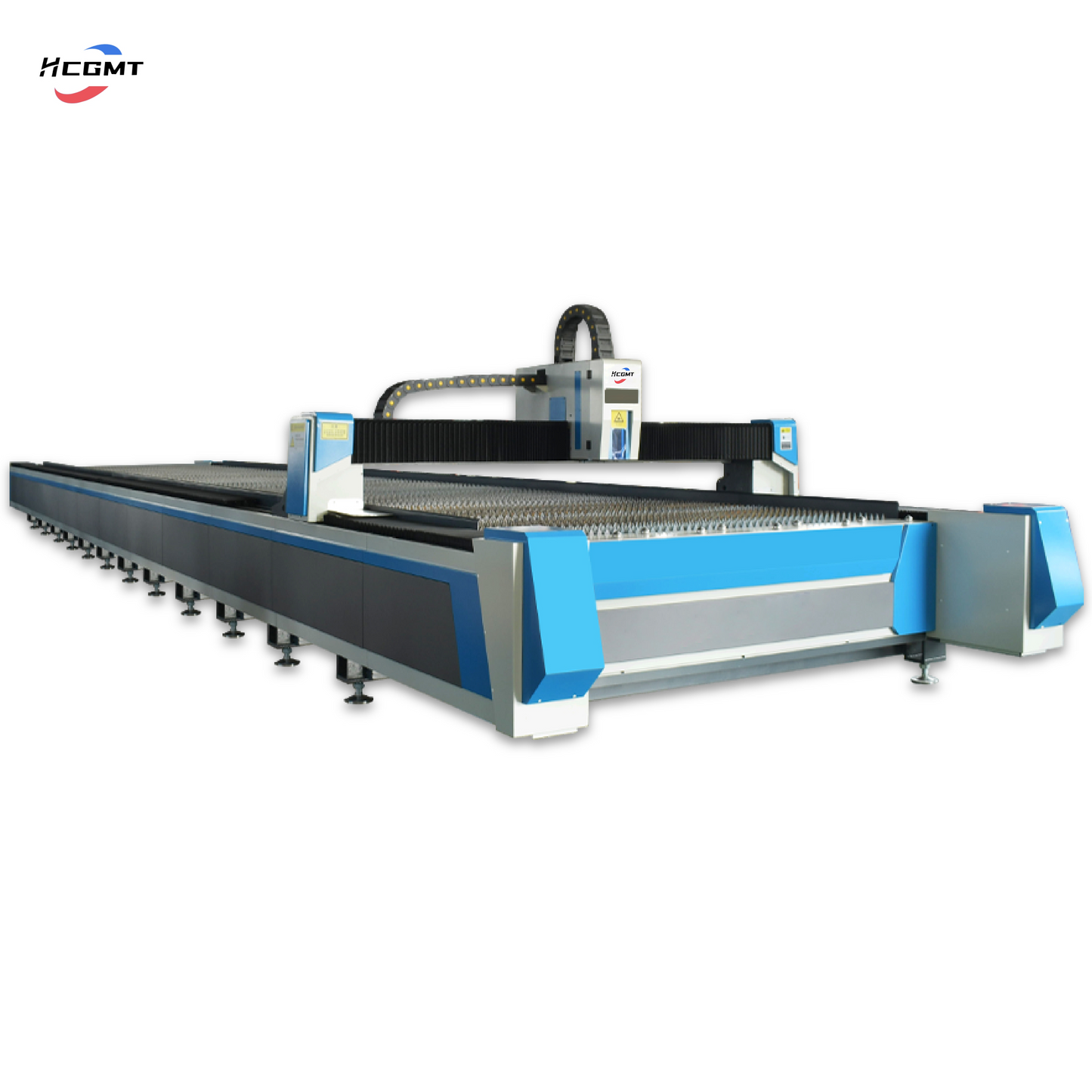
HCGMT® Oversized Workbench Fiber Laser Cutting Machine Customizable
HCGMT® Oversized Workbench Fiber Laser Cutting Machine Customizable
| JTM Oversized Workbench High-power Laser Cutting Machine Technical Parameters | |
| Laser Power | 15000W/20000W/30000W |
| Maximum Cutting Range | 8*2.5M/13*2.5M/13*3.2M/26*2.5M/26*3.2M |
| Maximum Moving Speed | 100M/MIN |
| Maximum Acceleration | 1.2G |
| Positioning Accuracy | 0.1MM |
| Repositioning Accuracy | 0.02MM |
| Working Voltage | 380V/50HZ |
| Cooling Type | Water Cooling |
| Note: All parameters are dynamic and for reference only. For more information, please contact customer service. | |
| Cutting Thickness & Speed Parameters | |||||||
| Material | Thickness(MM) | Gas | 1500W | 3000W | 6000W | 12000W | 15000W |
| Carbon Steel (Q235B) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | ||
| 1 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 26-29 | 47-50 | 58-62 | |||
| 2 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 7-8 | 21-23 | 31-36 | |||
| 3 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | / | 6-12 | 18-22 | 32-38 | 34-39 | |
| Oxygen | 2.9-3.2 | 3.9-4.1 | / | / | / | ||
| 4 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | / | / | 11-13 | 22-26 | 25-29 | |
| Oxygen | 2.4-2.6 | 3.4-3.6 | 3.7-4 | / | / | ||
| 5 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | / | / | 8-10 | 17-20 | 18-22 | |
| Oxygen | 1.8-2.0 | / | 3.2-3.3 | / | / | ||
| 6 | Air | / | / | 5.5-6.5 | 12-14 | 16-18 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | 5.5-6.5 | 11-13 | 15-17 | ||
| Oxygen | 1.6-1.8 | 2.7-2.8 | 2.6-2.8 | 2.6-2.8 | 2.6-2.8 | ||
| 8 | Air | / | / | / | 8-10 | 10-11 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 7-9 | 9-10 | ||
| Oxygen | 1.1-1.3 | 2.1-2.3 | 2.5-2.6 | 2.5-2.6 | 2.5-2.6 | ||
| 10 | Air | / | / | / | 5-6 | 7-8 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 4.5-5.5 | 6.5-7 | ||
| Oxygen | 0.9-1.0 | 1.4-1.6 | 2.2-2.3 | 2.2-2.3 | 2.2-2.3 | ||
| 12 | Air | / | / | / | 4.2-5 | 5.5-6.5 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 4-4.8 | 5-6 | ||
| Oxygen | 0.8-0.9 | 1-1.1 | 1.8-2.0 | 1.9-2 | 1.9-2 | ||
| 14 | Air | / | / | / | 3.5-4.2 | 5-5.55 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 3.2-3.5 | 4.8~5 | ||
| Oxygen | 0.6-0.7 | 0.9-0.95 | 1.4-1.7 | 1.5-1.6 | 1.5-1.6 | ||
| 16 | Air | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Oxygen | 0.5-0.6 | 0.8-0.95 | 1.2-1.3 | 1.4-1.6 | 1.4-1.6 | ||
| 18 | Air | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Oxygen | / | 0.7-0.72 | 0.7-0.8 | 1.4-1.5 | 1.4-1.5 | ||
| 20 | Air | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Oxygen | / | 0.6-0.65 | 0.6-0.65 | 1.4-1.5 | 1.4-1.5 | ||
| 22 | Oxygen | / | 0.55 | 0.55-0.6 | 1.2 | 1.2-1.3 | |
| 25 | Oxygen | / | 0.5 | 0.5-0.55 | 1 | 1.2-1.3 | |
| 30 | Oxygen | / | / | / | 0.4 | 0.8~0.9 | |
| 35 | Oxygen | / | / | / | 0.35 | 0.4 | |
| 40 | Oxygen | / | / | / | 0.3 | 0.35 | |
| 45 | Oxygen | / | / | / | 0.2 | 0.25 | |
| 50 | Oxygen | / | / | / | / | 0.2 | |
| 60 | Oxygen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 70 | Oxygen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 80 | Oxygen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Stainless Steel (SUS 304) | Thickness(MM) | Gas | 1500W | 3000W | 6000W | 12000W | 15000W |
| Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | |||
| 1 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 27-30 | 50-53 | 59-65 | / | / | |
| 2 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 8-9 | 23-25 | 32-38 | / | / | |
| 3 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 4.2-4.5 | 10-12 | 20-24 | 32-38 | 34-39 | |
| 4 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 2.0-2.2 | 6-8 | 12-15 | 22-26 | 25-29 | |
| 5 | Nitrogen/Oxygen | 1.5-1.7 | / | 9-11 | 17-20 | 18-22 | |
| 6 | Air | 1.0-1.2 | 2.9-3.1 | 6-7.5 | 14-16 | 17-20 | |
| Nitrogen | 1.0-1.2 | 2.9-3.1 | 6-7.5 | 13-15 | 16-19 | ||
| 8 | Air | 0.5-0.6 | 1.2-1.3 | 4-4.5 | 10-12 | 12-14 | |
| Nitrogen | 0.5-0.6 | 1.2-1.3 | 4-4.5 | 9-11 | 11-13 | ||
| 10 | Air | / | 0.75-0.8 | 2.2-2.4 | 8-9 | 8-10 | |
| Nitrogen | / | 0.75-0.8 | 2.2-2.4 | 7.5-8 | 7-9 | ||
| 12 | Air | / | 0.5 | 1.3-1.5 | 6.0-6.5 | 7.0-7.5 | |
| Nitrogen | / | 0.5 | 1.3-1.5 | 5.2-6.0 | 6.0-6.5 | ||
| 14 | Air | / | / | 0.9-1.0 | 3.7-4.0 | 4.8-5.0 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | 0.9-1.0 | 3.2-3.5 | 4.3-4.5 | ||
| 16 | Air | / | / | 0.8-0.85 | 2.7-3.0 | 3.4-3.8 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | 0.8-0.85 | 2.3-2.5 | 3.0-3.5 | ||
| 18 | Air | / | / | / | 2.2-2.5 | 3.0-3.3 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 1.8-2.0 | 2.6-2.8 | ||
| 20 | Air | / | / | 0.5-0.6 | 1.6-1.8 | 2.0-2.2 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | 0.5-0.6 | 1.3-1.5 | 1.6-1.8 | ||
| 25 | Air | / | / | / | 0.8-1.0 | 1.2-1.5 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 0.7-0.8 | 1.1-1.3 | ||
| 30 | Air | / | / | / | 0.65 | 0.6-0.7 | |
| Nitrogen | / | / | / | 0.25 | 0.33-0.35 | ||
| 35 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 40 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | 0.15 | 0.25 | |
| 50 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | 0.1 | 0.15 | |
| 60 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | / | 0.1 | |
| 70 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | / | 0.06 | |
| 80 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 90 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 100 | Nitrogen | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Aluminum | Thickness(MM) | Gas | 1500W | 3000W | 6000W | 12000W | 15000W |
| Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | |||
| 1 | Nitrogen/Air | 21-23 | 40-43 | 43-46 | / | / | |
| 2 | Nitrogen/Air | 5-7 | 16-18 | 26-28 | / | / | |
| 3 | Nitrogen/Air | 3.2-3.5 | 8-10 | 6-6.5 | 27-30 | 28-32 | |
| 4 | Nitrogen/Air | 1.5-1.7 | 5-6 | 4.5-5 | 19-21 | 20-22 | |
| 5 | Nitrogen/Air | 0.5-0.7 | / | 2.8-2.9 | 14-16 | 16-18 | |
| 6 | Nitrogen/Air | / | 1.5-2 | 1.7-1.8 | 10-12 | 12-14 | |
| 8 | Nitrogen/Air | / | 0.6-0.7 | 1.0-1.2 | 7-8 | 8-9 | |
| 10 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 0.7-0.9 | 4-5 | 5.5-6 | |
| 12 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 0.5-0.6 | 2.5-3 | 3.5-4 | |
| 14 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 2.3-2.5 | 2.5-3 | |
| 16 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 1.6-1.8 | 1.8-2 | |
| 18 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 1-1.2 | 1.4-1.6 | |
| 20 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 0.8 | 0.9-1.0 | |
| 22 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 0.5 | 0.8 | |
| 25 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | / | 0.5 | |
| 30 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 40 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 50 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Brass | Thickness(MM) | Gas | 1500W | 3000W | 6000W | 12000W | 15000W |
| Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | Speed (M/MIN) | |||
| 1 | Nitrogen/Air | 18-20 | 37-40 | 41-43 | |||
| 2 | Nitrogen/Air | 4-5 | 14-16 | 24-26 | |||
| 3 | Nitrogen/Air | 2.3-2.5 | 7-9 | 13-14 | 25-28 | 25-29 | |
| 4 | Nitrogen/Air | 1.2-1.4 | 3-4 | 9-10 | 16-18 | 18-20 | |
| 5 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 5-6 | 12-14 | 13-16 | |
| 6 | Nitrogen/Air | / | 1.2-1.5 | 4-4.5 | 9-11 | 11-13 | |
| 8 | Nitrogen/Air | / | 0.5-0.6 | 2.3-2.5 | 6-7 | 7-8 | |
| 10 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 1.5-1.6 | 3.5-4.5 | 5-5.5 | |
| 12 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 1.0-1.2 | 2.2-2.8 | 3.2-3.5 | |
| 14 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 0.7-0.9 | 1.8-2 | 2.3-2.8 | |
| 16 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | 0.5-0.6 | 1.4-1.6 | 1.5-1.8 | |
| 18 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 0.8-1.0 | 1.1-1.3 | |
| 20 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 0.7 | 0.7-0.9 | |
| 22 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | 0.4 | 0.7 | |
| 25 | Nitrogen/Air | / | / | / | / | 0.4 | |
| 1. In the cutting data, the core diameter of the output fiber of the 1500W laser is 50 microns. | |||||||
| 2. This cutting data uses Jia qiang cutting head, and the optical ratio is 100/125(focallength of collimating focusing lens) . | |||||||
| 3. Cutting auxiiary gas:liquidoxygen(purity99.99%), liquid nitrogen(purity 99.999%) , air(oil, water and filtration) . | |||||||
| 4. The air pressure in this cutting data specifically refers to the monitored air pressure at the cutting head. | |||||||
| 5. Due to diference sin various equipment configurations and cutting processes(machine tools, water cooling, environment, cutting gas nozzles, gas pressure, etc.) used by different customers. | |||||||
| 6. All parameters are dynamic and for reference only. For more information, please contact customer service. | |||||||
Ultra-large Workbench High-power Fiber Laser Cutting Machine can be divided into laser generation system, motion control system, and auxiliary system.
Laser Generation System
The laser generation system is the core part of the fiber laser cutting machine, mainly consisting of fiber laser, cooling system, power supply system, and control system.
Fiber Laser: Fiber laser is a device for generating laser, and its core component is erbium-doped fiber. Erbium-doped fiber is a special fiber that dopes erbium ions into the quartz fiber. It can absorb external pump light energy and be excited to the excited state. When the erbium ions in the excited state return to the ground state, they will release energy and form laser oscillation to generate laser output. Depending on the requirements, fiber lasers can output different wavelengths, such as 1064nm, 1080nm, etc.
Cooling System: To prevent the fiber laser from being damaged by overheating during operation, a cooling system is needed for heat dissipation. Common cooling methods include water cooling, air cooling, and liquid nitrogen cooling. Water cooling is achieved by immersing the fiber laser in cooling water for heat dissipation; air cooling is achieved by blowing cooling air for heat dissipation; liquid nitrogen cooling is achieved by spraying liquid nitrogen on the surface of the fiber laser for heat dissipation. Depending on the power and specification of the fiber laser, a suitable cooling method can be selected.
Power Supply System: The fiber laser requires a stable power supply to maintain its normal operation. The power supply system is responsible for providing power to the fiber laser, including different power supply options such as commercial power and UPS. At the same time, the power supply system also needs to filter and regulate the power supply to ensure the stable operation of the fiber laser.
Control System: The control system is one of the key parts to achieve high-precision and high-efficiency cutting of the ultra-large workbench high-power fiber laser cutting machine. The control system mainly controls and adjusts through a computer, which can control parameters such as laser output power, cutting speed, spot shape and size. The control system also includes different sub-systems such as displacement control system, speed control system, and power control system to achieve comprehensive cutting control.
Motion Control System
The motion control system is an important part of the fiber laser cutting machine, mainly controlling the movement path and speed of the laser cutting head. The system is usually composed of a computer numerical control (CNC) system and a motion controller.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) System: The CNC system is the core of the motion control system. It can accept and process the cutting path information and other relevant parameters input by the user, and then convert this information into motion instructions that the machine tool can understand. This includes three axial movements of X, Y, and Z to ensure that the laser cutting head can move along the preset path, while controlling the cutting speed to achieve the best cutting effect. These instructions are executed through the motion controller to achieve precise motion control of the machine tool. The accuracy and stability of the CNC system directly affect the cutting quality.
Motion Controller: The motion controller is an intermediate link between the CNC system and the machine tool, responsible for receiving the motion instructions issued by the CNC system and converting them into signals that the machine tool can understand. The motion controller typically uses servo motors and transmission components such as leadscrews or gears to drive the movement of the cutting head. Servo motors are devices that can precisely control rotation, and through components such as leadscrews or gears, they can convert this rotation into linear movement of the cutting head.
In the process of fiber laser cutting, the motion control system needs to work together with other parts such as the laser generation system and the cutting head system. For example, the laser generation system needs to provide stable laser output to meet the requirements of the cutting speed, and the cutting head system needs to accurately perform the cutting operation to ensure cutting accuracy. In actual operation, users need to select appropriate cutting parameters such as cutting speed and laser power according to different cutting requirements and material characteristics.
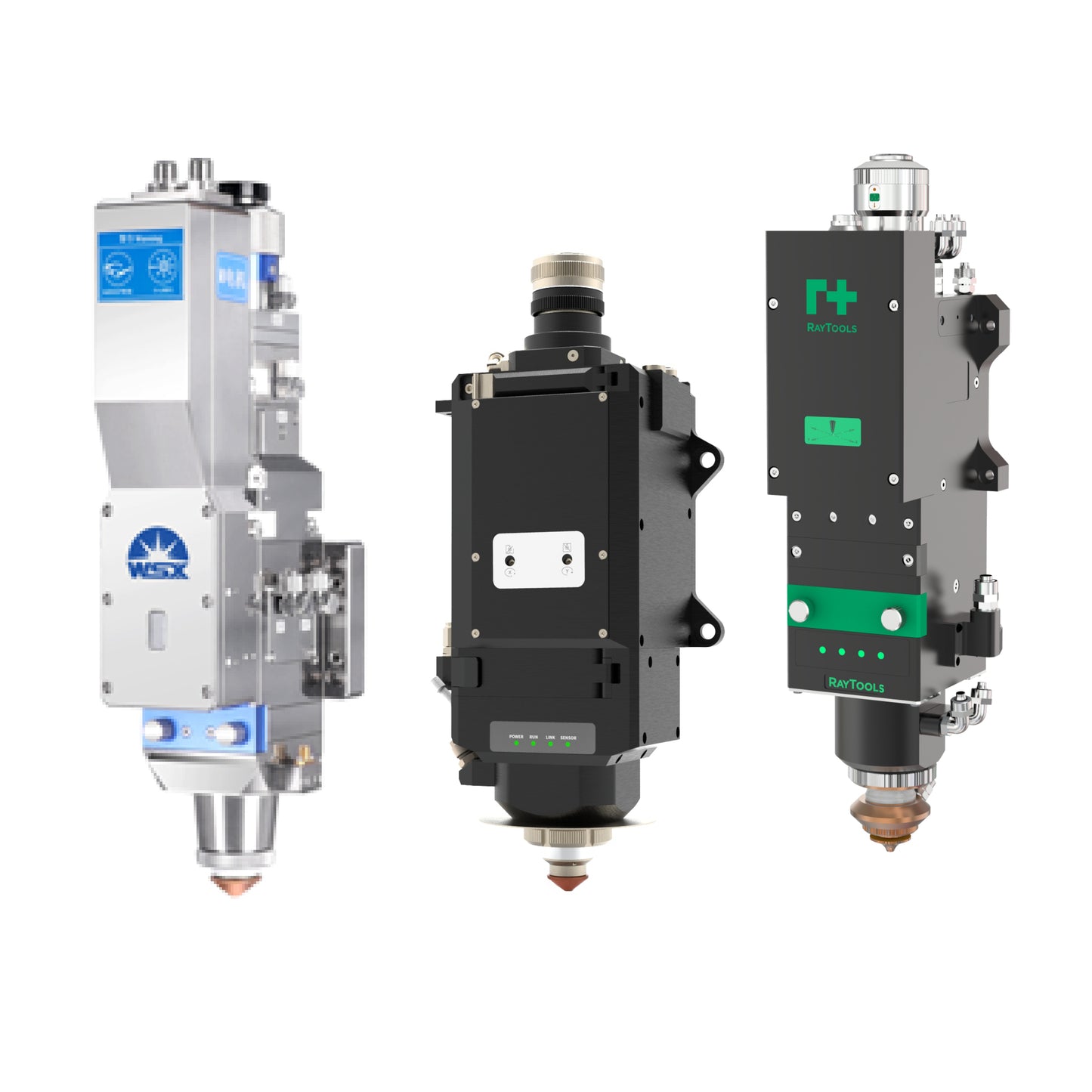
Cutting Head System
The cutting head system is a key part of the fiber laser cutting machine, mainly consisting of the cutting head, focusing lens, and auxiliary gas nozzle. The cutting head is used to load the focusing lens to achieve focusing of the laser beam. The focusing lens focuses the laser beam into a tiny spot to achieve precise cutting. The auxiliary gas nozzle is used to cool the metal surface and blow away the molten slag during the cutting process.
Cutting Head: The cutting head is one of the important components of the fiber laser cutting machine. It is mainly used to load the focusing lens to achieve focusing of the laser beam. The cutting head is usually composed of high-precision optical and precision mechanical components, capable of focusing the laser beam into a tiny spot to achieve precise cutting.
Focusing Lens: The focusing lens is a key component in the cutting head. It is used to focus the laser beam into a tiny spot. The focusing lens is usually made of high-quality glass or quartz materials, with high transparency, heat resistance, and stability. In the laser cutting process, the focusing lens can focus the laser beam onto the surface of the metal material, forming a high-temperature and high-pressure laser beam to melt and blow away the metal material.
Auxiliary Gas Nozzle: The auxiliary gas nozzle is another important component in the cutting head system. During the cutting process, the auxiliary gas nozzle is used to spray auxiliary gas onto the metal surface to cool it and blow away the molten slag, etc. The auxiliary gas mainly reduces the temperature during the cutting process, reduces thermal deformation, and prevents oxidation of the metal material. At the same time, the auxiliary gas can also blow away the molten slag from the cutting area, improving the cutting quality and efficiency.
In the fiber laser cutting machine, the precision and stability of the cutting head system directly affect the cutting quality and efficiency. Therefore, in the process of use, it is necessary to regularly check and maintain the cutting head system to ensure that its performance indicators are normal. At the same time, different specifications and types of focusing lenses and auxiliary gas nozzles can be replaced according to different cutting requirements to achieve more efficient and flexible cutting operations.
The detailed operation process is as follows:
Positioning and Fixing of Metal Plate: Place the metal plate to be cut on a workbench that can withstand the impact of the high-power laser beam and fix it to ensure that the metal plate will not move or deform during the cutting process. This workbench should have high heat capacity and good thermal conductivity to effectively absorb and dissipate the energy of the laser beam.
Selection and Adjustment of Fiber Laser: Select an appropriate high-power fiber laser according to the thickness, material, and cutting requirements of the metal plate and adjust it to the appropriate power and pulse width. Generally speaking, the output power of a high-power fiber laser can be anywhere between a few kilowatts to several kilowatts, and the pulse width can be adjusted according to needs. For cutting large metal plates, it is usually necessary to choose a high-power and short-pulse laser to cut the metal plate in a short time.
Planning of Cutting Path: Use CAD software to input the shape and size of the metal plate to be cut into a computer and generate the cutting path. This path should take into account the shape, size, and placement of the metal plate, as well as the maximum cutting speed and accuracy of the fiber laser. When planning the cutting path, it should minimize the number of times the laser beam moves and travels empty to improve the cutting efficiency.
Exchange of Dual Workbenches: Another feature of high-power dual-workbench fiber laser cutting machines is the dual workbench design. During the cutting process, when one workbench is completed, the control system will automatically control the exchange of workbenches, place a new metal plate on the already cut workbench, and continue the cutting operation. This process can be completed in a short time, thereby improving the efficiency of the entire cutting process.
Our core product, the high-power dual-worktable fiber laser cutting machine, stands out in the industry with its unique design and advanced performance. This equipment adopts fiber laser technology, characterized by high speed, high precision, and high stability. It is also equipped with an intelligent operating system that makes the cutting process simpler and more efficient. It is widely applicable for cutting various metal materials such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper, etc., meeting the demand for efficient and high-precision cutting in industrial production.
Our high-power dual-worktable fiber laser cutting machine not only leads the technology field but also has an extremely high cost-effectiveness. We always adhere to the customer needs-oriented approach, while emphasizing product quality and performance, we also pay close attention to the actual costs of customers. Our equipment adopts advanced production processes and high-quality materials to ensure the durability and stability of the equipment, while also ensuring that its price is more competitive compared to similar products.
Share with